KTIRADS
2022. 10. 1. 18:07ㆍ초음파/갑상선 및 경부 초음파
728x90





0068KJR_kjr-22-1569.pdf
0.14MB









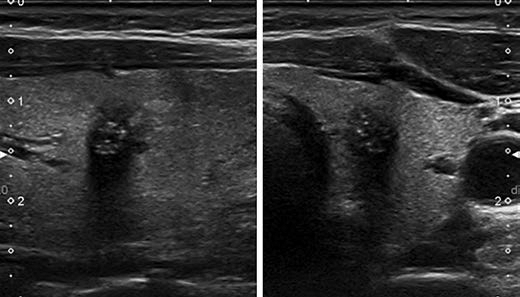



'초음파 > 갑상선 및 경부 초음파' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 갑상선 유두암 증례 (0) | 2023.02.16 |
|---|---|
| 갑상샘 초음파 검사에서 K-TIRADS 점수화 체계를 사용한 양성과 악성 갑상샘 결절의 감별진단 (0) | 2022.10.02 |
| 갑상성 초음파 1장 정리_김일봉 원장님 강의 (0) | 2022.09.20 |
| 갑상선 결절의 w/u flow chart (0) | 2022.04.19 |
| 2021 K-TIRADS 갑상선 결절에 대한 w/u (0) | 2022.02.25 |